IQIRVO efficacy1
The only pivotal study for PBC in which
40% of patients had baseline ALP >3 x ULN2
The ELATIVE® trial was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of IQIRVO in patients with PBC and inadequate response or intolerance to UDCA.1
- Placebo + UDCA referred to as “UDCA alone”
- 95% (153/161) of patients on IQIRVO in the ELATIVE trial received concurrent UDCA therapy1
- ULN for ALP was defined as 104 U/L for women and 129 U/L for men1
|
Baseline characteristics2 |
IQIRVO + UDCA |
UDCA alone |
OLE crossovera |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sex, female % |
94 |
98 |
98 |
|
Age <65 years % |
76.9 |
81.1 |
|
|
Years since |
7.9 |
8.3 |
9.5 |
|
Mean (±SD) |
321.3 (121.9) |
323.1 (198.6) |
335.8 (187.9) |
|
ALP >3 x ULN % |
39.8 |
37.7 |
42.2 |
|
Mean (±SD) baseline total bilirubin mg/dL |
0.57 |
0.55 |
0.64 |
|
Mean PBC WI-NRS score |
3.3 |
3.2 |
|
|
Mean liver stiffness kPa |
9.9 |
10.7 |
|
|
Liver stiffness |
34 |
38 |
31 |
|
Osteoporosis % |
19 |
4 |
|
~41% of patients had moderate-to-severe pruritus3
~35% started the trial with advanced disease2,3,b
First second-line PBC treatment in which 13x more patients achieved biochemical response vs UDCA alone1
Biochemical response at 52 weeks1:
ALP <1.67 x ULN
ALP decrease ≥15% from baseline
Total bilirubin ≤ ULN
cSix patients in the IQIRVO group took IQIRVO alone, while 2 patients in the UDCA group took placebo alone.1
dALP values are based on a weighted average of the ULN; 105 U/L is the weighted ULN based on a ULN of 129 U/L for men and 104 U/L for women.1
Biochemical response at week 521,c
cSix patients in the IQIRVO group took IQIRVO alone, while 2 patients in the UDCA group took placebo alone.1
dALP values are based on a weighted average of the ULN; 105 U/L is the weighted ULN based on a ULN of 129 U/L for men and 104 U/L for women.1
Biochemical response across all subgroups2
Patients achieving biochemical response in a
subgroup analysis by baseline ALP2
Rapid ALP reduction as early as 4 weeks, sustained over 3 years2
ALP reduction from baseline2
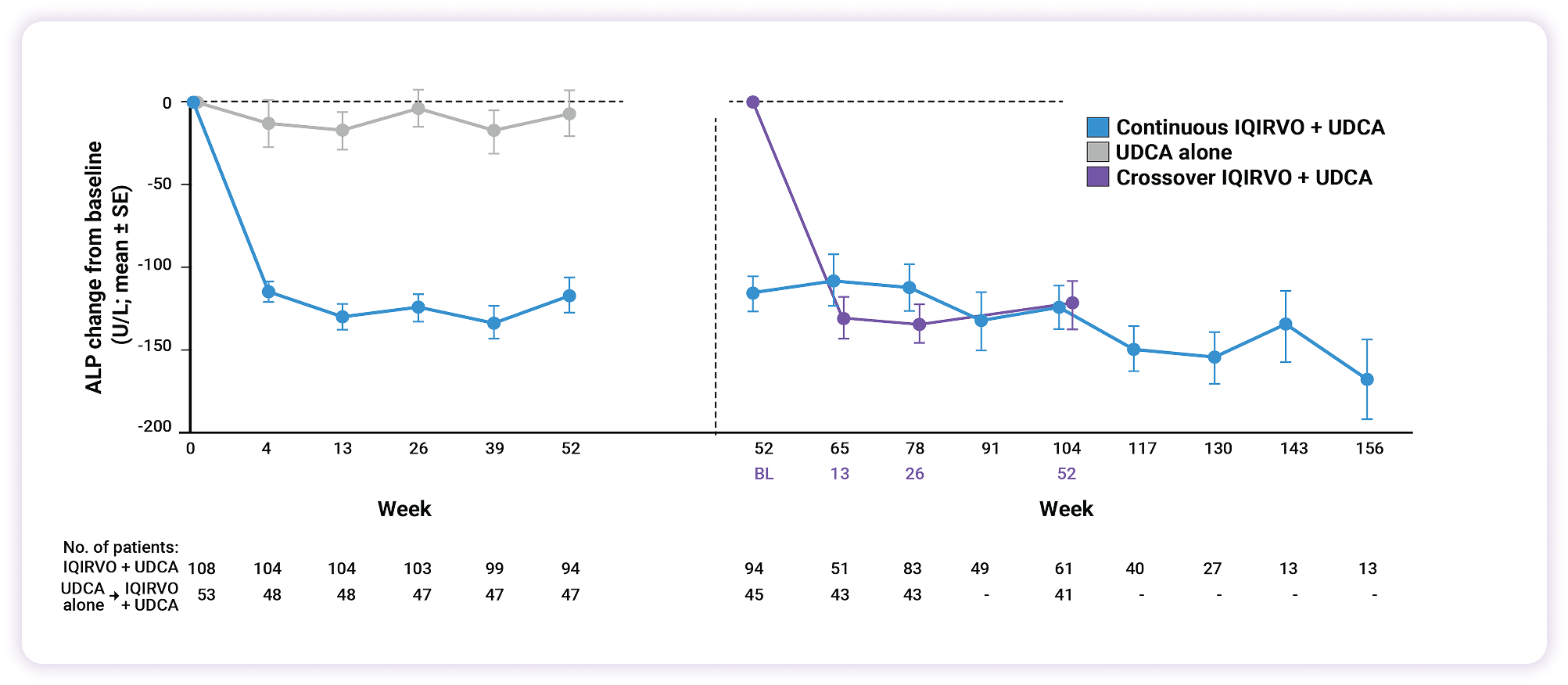
37% reduction in ALP
as early as 4 weeks with IQIRVO2
37% reduction in ALP
as early as 4 weeks with IQIRVO2
ALP reduction across subgroups Powerful ALP reduction, regardless of starting point2
Mean change from baseline to week 52 in ALP,
stratified by baseline ALP levels2

A 22x greater reduction in ALP with IQIRVO vs UDCA alone3
LS mean change from baseline: IQIRVO -117 U/L, UDCA -5.3 U/L3
Normalization at 52 weeks in a pivotal study1
Target an ALP of 105 U/L or lower—only with IQIRVO1,d
dALP values are based on a weighted average of the ULN; 105 U/L is the weighted ULN based on a ULN of 129 U/L for men and 104 U/L for women.1
More than half of patients with baseline ALP ≤2 x ULN achieved normalization2
Explore patient profiles
Helen age 42
Inadequate response to first-line treatment
Disease history
- 24 months since diagnosis
- Treated with UDCA (900 mg daily) for 24 months
- Current ALP 218 U/L (2.1 x ULN) vs 353 U/L (3.4 x ULN) at diagnosis4
- 220 U/L ALP at 6-month marker vs 240 U/L at 12 months after starting therapy
- Current bilirubin 0.56 mg/dL (normal) vs 0.56 mg/dL (normal) at diagnosis5
Risk factors for progression
- Inadequate response to first-line treatment6
- Age <45 at diagnosis6,7
ALP levels with first-line treatment
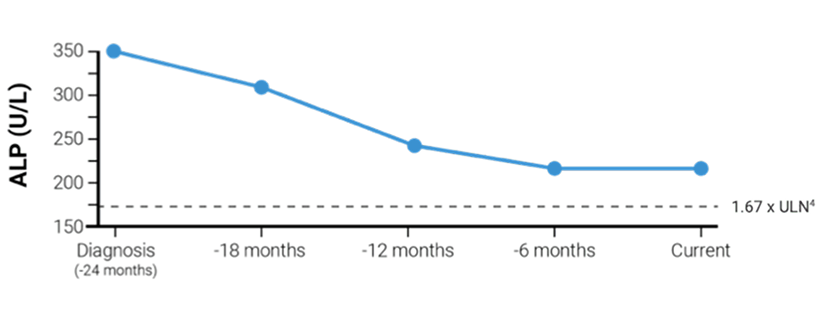
With IQIRVO, 15% of patients were able to achieve ALP normalization of 105 U/L or lower. Lowering ALP is a key treatment goal in managing PBC1,8,d
dALP values are based on a weighted average of the ULN; 105 U/L is the weighted ULN based on a ULN of 129 U/L for men and 104 U/L for women.1
Marie age 57
Unresponsive to current second-line treatment
Disease history
- 5 years since diagnosis
- Second-line treatment added 6 months ago, in combination with UDCA (prescribed at diagnosis)
- 5 years (UDCA), 1.5 years (UDCA + obeticholic acid)
- Recently reported symptoms of increased pruritus and fatigue
- Current ALP of 239 U/L (2.3 x ULN) vs 187 U/L (1.8 x ULN) at diagnosis4
IQIRVO could help patients like Marie achieve biochemical response1
aPatients completing the ELATIVE double-blind period were eligible to enter the OLE trial to receive IQIRVO 80 mg daily. Baseline in this OLE crossover arm was defined as the last available measurement before the first OLE IQIRVO dose.2
bLiver stiffness >10 kPa and/or bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis on histology.2
ALP=alkaline phosphatase; CI=confidence interval; OLE=open-label extension; PBC=primary biliary cholangitis; SD=standard deviation; SE=standard error; UDCA=ursodeoxycholic acid; ULN=upper limit of normal; WI-NRS=worst itch numeric rating scale.
References: 1. IQIRVO [package insert]. Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. Cambridge, MA. 2. Data on file. Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. 3. Kowdley KV, Bowlus CL, Levy C, et al; ELATIVE Study Investigators’ Group. Efficacy and safety of elafibranor in primary biliary cholangitis. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(9):795-805, suppl. 4. ALKP. Mayo Clinic Laboratories. Accessed February 6, 2025. https://www.mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/overview/622157#Clinical-and-Interpretive. 5. BILI3. Mayo Clinic Laboratories. Accessed February 6, 2025. https://www.mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/overview/8452#Clinical-and-Interpretive. 6. Hirschfield GM, Chazouillères O, Cortez-Pinto H, et al. A consensus integrated care pathway for patients with primary biliary cholangitis: a guideline-based approach to clinical care of patients. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15(8):929-939. 7. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: the diagnosis and management of patients with primary biliary cholangitis. J Hepatol. 2017;67(1):145-172. 8. Kowdley KV, Bowlus CL, Levy C, et al. Application of the latest advances in evidence-based medicine in primary biliary cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023;118(2):232-242.

